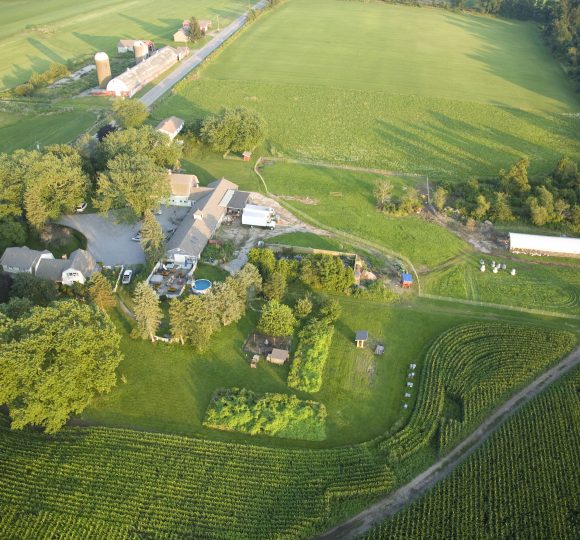
Kentucky is famous for its rolling bluegrass hills, diversified farms and world-class horse industry. Its rich farming heritage provides beautiful landscapes for residents and tourists, protects wildlife and water quality, and is the foundation for community and tradition in the Bluegrass state. Agriculture also plays an important role in local economies. According to the 2002 Census of Agriculture, Kentucky’s 86,541 farms cover 13.8 million acres and produce more than $3 billion of agricultural goods and services.
However, recent changes in the tobacco economy, an influx of new residents, rising land prices and other growth pressures threaten the future of Kentucky’s agriculture. Landowners are looking for ways to protect their investments and remain economically viable. For many farmers this may mean selling their land for development. But there are alternatives. Kentuckians take great pride in their agrarian heritage and place a high value on private land ownership, and fortunately they have a variety of options to help them stay on the land.
This guide provides an overview of the alternatives available to Kentucky landowners who want to pursue conservation options and benefit from financial incentives and technical assistance to save their land and improve its productivity. The information is presented in five sections:
I. Farmland Protection: to save farmland for future generations
II. Tax Reduction and Exemption: to level the playing field for agricultural landowners
III. Farm Enterprise Development: to help farmers create profitable new farm activities
IV. Land Conservation and Stewardship: to enhance wildlife and natural resources on private lands
V. Resources: contact information for agencies and organizations to help landowners achieve their agricultural and conservation goals