Soil Health Toolkit
- Basics
- Assessing Soil Health
- Benefits
- COMET Tools
- Engaging Producers and Landowners
- ACEs and Management Plans
- Technical and Financial Resources
- Ecosystem Markets
Soil Health Basics
Healthy soil can provide economic and agronomic benefits to a farm or ranch, as well as benefits to the surrounding ecosystems and communities. In promoting soil health, it is important for land protection practitioners to know the benefits and principles of soil health and the practices that build soil health. It’s worth keeping in mind that producers may face social, technological, and economic barriers when it comes to implementing new practices to improve soil health. The following information is adapted from American Farmland Trust’s Soil Health Stewards trainings on Soil Health Basics.
Learn about Soil Health
Soil is a living ecosystem made up of minerals, organic matter, and pore spaces containing air, water, dissolved nutrients, and living organisms. Healthy soils function better than degraded soils to serve human and ecosystem needs: they support agricultural production; filter and store water; “cycle” or move nutrients between the physical environment and living organisms; moderate temperature extremes; protect plants from pathogens and stress; store carbon and moderate the release of gases; prevent erosion; and provide habitat for soil organisms.
The USDA Natural Resources Conservation Service (NRCS) defines soil health as the soil’s continued capacity to function as a vital living ecosystem that sustains plants, animals, and humans. Healthy soils are more resilient and reduce risks such as erosion, flooding, drought, dust storms, and pests. Healthy soils are high in organic matter and more stable, enabling water from extreme rainfall to be stored for when it is needed by crops. Because they function better, healthy soils improve farmer profits by increasing and stabilizing yields, reducing input costs, and even providing opportunities for better markets.
.
Understand Soil Health Principles and Practices
The way farmers and ranchers manage their land impacts soil health. Soils that may be of marginal quality or degraded can be improved and restored using practices and systems of practices that build soil health (also referred to as regenerative practices, because the regenerate—or rebuild—soil function, rather than just maintaining it).
Principles
 For more than a decade, NRCS has promoted four principles to restore and protect soil health:
For more than a decade, NRCS has promoted four principles to restore and protect soil health:
- Minimize disturbance: this includes physical, biological, and chemical disturbance; reduce tilling and the use of chemical inputs, rotate grazing animals;
- Maximize soil cover: keep the soil surface covered with residue or live plants year-round;
- Maximize biodiversity: integrate diversity of plants, livestock and/or organic amendments; grow many different species of plants through rotations and diverse cover crop mixtures;
- Maximize continuous living roots: keep living crops and cover crops growing for as much of the year as possible.
Practices
Each principle is achieved through a range of associated conservation practices—specific land management strategies producers can implement to protect and restore natural resources.
The first two principles—minimizing disturbance and maximizing soil cover—protect the habitat for soil organisms. This can be achieved through reduced tillage, nutrient management, integrated pest management, prescribed grazing, and cover cropping. Together, these approaches increase soil organic matter, stabilize soil aggregates, mitigate temperature changes, reduce evaporation, and improve water infiltration and storage, which reduces the risk of erosion,
The second two principles—maximizing biodiversity and living root systems—aim to feed soil organisms. This can be accomplished by integrating livestock into a production system, growing different species of plants through rotations or a diverse mixture of cover crops, and creating dedicated grasslands. These practices increase biological activity and diversity belowground. They also increase soil organic matter and nutrient cycling and improve plant growth.
These soil health principles and practices also apply to grazing systems. Biodiversity, for example, can be built up through forage planting, while soil disturbance can be controlled with prescribed grazing. When forages are allowed to regrow and fields get adequate rest, grazing can be good for soils, improving aeration and aggregate stability.
A soil health management system is a collection of practices that increase soil carbon levels and improve soil health by applying the four soil health principles. When implemented together, and adapted as needed to different production systems, climates, and soil types, these principles can rebuild soils and restore their functions. What can be achieved through soil health management systems, and how a system needs to be adapted to a production system, depends on climate and soil type. For example, soils of loamy and clayey texture can store more organic matter and water than sandy soils but are also generally more prone to compaction and saturation, especially when they are degraded already. Sandy soils are more likely to be problematic in droughty conditions than loamy and clayey soils – but again, more so, if they are degraded.
Identify Barriers to Adoption
Producers and landowners may face multiple barriers when it comes to adopting soil health practices.
- For many, embracing new practices requires a new way of thinking.
- Often, a basic understanding of soil function and soil health benefits is required for a producer or landowner to choose to adopt soil-beneficial practices.
- Choosing to adopt new practices means acquiring the technical knowledge needed to implement new practices and management systems. It may also require new equipment and infrastructure.
- There may be a lack of community support for adoption of new or different practices.
- Finally, producers and landowners may worry about the financial impact of practice adoption.
You can help producers and landowners overcome these barriers by cultivating a relationship with the producer, offering information and helping organize educational opportunities around new practices, creating supportive networks, and connecting landowners and producers with technical experts. For more information, see the Engaging Producers and Landowners tab.
Assessing Soil Health
Standard soil tests can provide farmers with soil nutrient recommendations, indicating which nutrients the soil is lacking and which amendments should be applied to fields to correct for deficiencies. However, a standard soil nutrient test only tells part of the soil health story—other constraints that impact the ability of the soil to function well are not covered in such a test. A full soil health assessment looks at the biological and physical functioning of the soil in addition to the nutrient levels.
A soil health indicator is a soil property that provides information about the status of specific soil processes. There are two methods of assessing indicators: an in-field assessment is a qualitative or semi-quantitative measurement and assesses indictors on the spot; a laboratory assessment measures quantitative indicators and is better for monitoring soil health over time.
The following information is adapted from American Farmland Trust’s Soil Health Stewards training on Soil Health Assessment.
Learn about In-Field Soil Health Assessment
NRCS staff or other trained soil health professionals can assist with assessing soil health in the field. This will include a field visit, a conversation with the farmer on management, and use of the NRCS web soil survey. The web soil survey provides information on soil’s inherent properties such as soil texture, slope, and water table. While this is useful for gauging a “baseline,” management is the primary driver of soil degradation. When looking at indicators of soil health in the field, it is important to keep in mind both the soil properties and the management practices being used. Some indicators show the presence of well-functioning soils while others can point to soil degradation. Below are six of the major indicators to look for when assessing soil health in the field:
- Aggregate stability is one indicator of soil health. Soil aggregate stability is the ability of the soil to stick together and resist raindrop impact and erosion. To assess aggregate stability in the field, one can conduct a slake test, a strainer test, or a Jornada soil aggregate stability test. These tests reveal healthy soils if at least 80% of the soil mass remains intact in a slake test; if the sample “stands up” for strainer test and runoff water is translucent; or if it meets the Jornada test criteria.
-
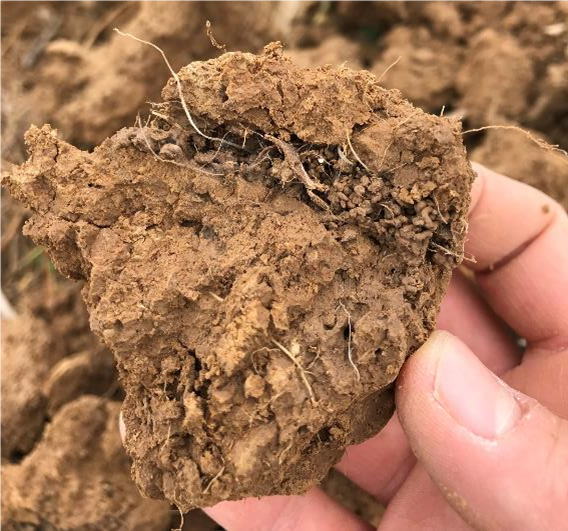

Plant roots and soil biopores NRCS USDA Plant roots and biopores are another feature of healthy soils. Roots influence the soil immediately adjacent to them through exudates, growing and leaving soil organic matter as they die. Root systems and root channels can help address aggregate instability, soil organism habitat loss or degradation, and soil organic matter depletion. To assess this indicator of soil health in the field, look for evidence of dark root channels or biopores left by previous plants or earthworms.
- Adequate soil cover promotes healthy soils. Soil cover is the percent of the soil surface that is covered by plant residue, organic mulch, or live plants. Having adequate soil cover can help address aggregate instability, soil organism habitat loss or degradation, soil organic matter depletion, and compaction. Soil cover can be measured in the field using farmer interview, the photo estimation method, or the line intercept method. If the soil is more than 75% covered after planting, it meets the criteria for adequate soil cover.
- Surface crusts indicate soils with weak aggregate stability. Soil crusts form after rain or irrigation and can be evaluated by visual observation. Note whether crusts are throughout the field or only in patches. Near the surface, the soil will be dense and show layered sediment deposits. Poor crop emergence and uneven stand are also signs of surface crusts. Healthy soils should have surface crusts on 5% or less of the field.
- Ponding can be another indicator of poor soil health. Ponding involves areas of the field that collect and hold runoff water from other parts of the field. Ponding may play a role in aggregate instability and surface compaction. Ponding can be identified by farmer interview or visual observation after rainfall or irrigation. Evidence of crop residue deposits and poor crop conditions, especially yellowing, may also point to ponding. Healthy soils should show evidence of ponding no more than 24 hours after a typical rain event.

Platy soils NRCS USDA - Penetration resistance, or management-induced reduction of large pores and degraded structure (i.e., platy) results in a decrease in root depth, plant growth, and soil biological habitat and activity. Penetration resistance is an indicator of aggregate instability, organic matter depletion, and surface compaction. To assess this feature of soil structure, one can evaluate multiple representative locations in the field, ideally when the soil moisture is near field capacity, and record the depths of restrictive layers and PSI readings using a penetrometer or by feeling for resistance with an irrigation flag. One can also look at root development and distribution and check for platy structure. In healthy soils, this evaluation should reveal granular structure, appropriate PSI readings, and vertical channels or roots. Healthy roots show unrestricted root growth and may have many fine roots.
For further description and images of these soil health indicators, see the NRCS Cropland In-Field Soil Health Assessment Guide Technical Note.
Learn about Laboratory Soil Health Assessment
Lab tests will look for different indicators of soil health than a field assessment. These indicators are standardized and have been chosen for their agronomic relevance. A laboratory test for soil health may evaluate these indicators:
- Soil structural stability and water partitioning. An indicator of aggregate stability, this is an important part of water infiltration and water capacity.
- Soil organic matter cycling is an indicator of soil organic carbon. This assists with carbon cycling and sequestration.
- Carbon food source, as permanganate oxidizable carbon (or active carbon). This active carbon is a source of food for essential soil organisms.
- Microbial activity is an indicator of short-term carbon mineralization, or respiration. This reflects organism activity in the soil.
- Bioavailable nitrogen is an acid citrate extractable protein. This is an indicator of an organically bound, environmentally stable soil nitrogen pool.
For more information on lab indicators of soil health, see the NRCS Technical Note on Recommended Soil Health Indicators and Associated Laboratory Procedures.
Soil health indicator results have to be interpreted with regional (climate and soil type) considerations in mind. Interpretations have been improving over time and are now available for most indicators through the NRCS Soil Testing Conservation Activity 216, supported by NRCS’ Environmental Quality Incentives Program.
Recognize and Address Soil Health Resource Concerns
Once the properties of the soil have been identified through in-field or laboratory assessment, one can begin to address soil health resource concerns. NRCS defines a resource concern as “an existing or expected degradation of the soil, water, air, plant, or animal resource base to the extent that the sustainability or intended use of the resource is impaired.” Soil resource concerns include compaction, organic matter depletion, soil organism habitat loss or degradation, and aggregate instability.
These concerns can be addressed through soil health management planning. There are both short-term and long-term management options for improving soil health. For example, if the soil displays poor aggregate stability, this could be addressed immediately by incorporating fresh organic materials into the soil, using shallow-rooted crops or cover crops in these areas, and adding manure, green manure, or mulch to the field. Longer-term means of improving aggregate stability include reducing tillage, using surface mulch on fields, and using a rotation of sod crops and mycorrhizal host plants. Once the appropriate management practices have been implemented in the field, the next steps are to observe the effects of the new practices and fine tune practices as needed. Conducting soil health assessments periodically allows for ongoing improvement to soil health as management practices are further refined and continually adapted to address the current conditions of the soil.
Measuring Soil Health Economic and Environmental Benefits
Research suggests that implementing practices such as no-till or reduced tillage, cover cropping, nutrient management, and conservation crop rotation can improve soil health, reduce runoff, lower greenhouse gas emissions, and sequester carbon. Information on the economic benefits associated with soil health is also important to those in the agricultural community, including growers, landowners, agricultural retailers, bankers, and corporations with sustainability goals, for whom knowing the “bottom line” is important to making decisions. The following information is adapted from American Farmland Trust’s Soil Health Stewards trainings on Soil Health Benefits.
Use the Soil Health Case Studies
The AFT-NRCS Soil Health Case Studies estimate the economic effects of implementing soil health practices by looking at the costs, benefits, and return on investment experienced by farmers who have adopted one or more soil health practices. The environmental impacts of soil health practices were estimated by looking at water quality and changes in greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions. The findings from these case studies are intended to give farmers confidence in adopting practices that have the potential to increase farm viability, improve resiliency, address climate change, and lessen agriculture’s impact on water resources.
These case studies can be a useful tool when talking with producers about the potential economic benefits and costs of implementing soil health practices on their operation. AFT also produced the Farmers’ Guides to Soil Health Economics, a series of two-page guides for producers summarizing findings from relevant economic studies in an easy-to-read format.
The economic impacts of soil health practices
The AFT-NRCS Soil Health Case Studies find that soil health-successful farmers may experience net economic benefits, which can be achieved in two ways—through increases in income, decreases in costs, or a combination of the two. Increases in income can be attributed to yield increases. Decreases in costs, meanwhile, can be attributed to reduced fertilizer and herbicide costs, fewer machine passes (which reduces fuel, repair, and operating expenses), reduced field repairs, and less soil erosion.
The case studies demonstrate that net return on investment varies from farm to farm. In some instances, the economic benefits of implementing soil health practices may be offset by decreases in income due to increased costs. Increases in cost may be attributed to variable rate application, increased soil testing, learning costs associated with the transition in soil health management, new machinery, and costs associated with implementing cover crops, including seed, planting, and harvest costs.
The economic impacts of implementing soil health practices on case study farms are derived using a Partial Budget Analysis (PBA). A PBA estimates the economic effect—both benefits and costs—of variables affected by a change in a farming operation. For the Soil Health Case Studies, the PBA compares costs and benefits “before” and “after” soil health practice implementation. To conduct this PBA, AFT developed a Retrospective Soil Health Economic Calculator (R-SHEC). R-SHEC is an Excel-based tool that can be used to quantify the benefits and costs experienced by already “soil health successful” producers. The Predictive Soil Health Economic Calculator (P-SHEC), meanwhile, can be used by practitioners, conservation professionals, and farmers to estimate the potential long-term costs and benefits of adopting certain soil health practices. AFT also produced case studies using Cornell University’s Dairy Farm Business Summary (DFBS) survey.
The environmental impacts of soil health practices
In addition to the benefits to individual farm and ranch operations, improving soil health can also provide environmental benefits. Healthy soils have the capacity to store more carbon, thereby mitigating climate change. Greater infiltration and water holding capacity mean that health soils can reduce runoff, leading to improved water quality. Increased soil stability can also reduce flood damage in surrounding communities.
The Nutrient Tracking Tool can estimate reductions in nitrogen, phosphorus, and sediment losses associated with implementing soil health practices. Climate benefits can be evaluated with the help of COMET-Farm, which estimates the ‘carbon footprint’ for all or part of a farm or ranch operation. It also allows users to evaluate different options for reducing emissions and sequestering more carbon.
Farmers and ranchers in arid regions may face challenges with implementing soil health practices—especially cover crops—due to limited water availability. Farmers in water-limited environments may need to weigh the environmental and financial pros and cons of implementing new practices. The environmental benefits of implementing cover crops in water-limited areas may be especially pronounced: in areas prone to drought, cover crops can be a means of improving water holding capacity and water infiltration. There is, however, potential for cash crops to produce less if cover crops draw down soil moisture levels. So while cover crops do improve soil health in arid environments, it can be tricky to figure out where and how they can be economically most beneficial. Creative solutions, such as integrating grazing cover crops, can make up for reduced cash crop yield.
COMET Tools
Soil health management practices, such as no-till and cover cropping, can build carbon levels in the soil in the form of soil organic matter. This organic matter provides nutrients for plants, improves soil structure, helps hold water, and moderates pathogen and pest pressure. These practices also have the potential to reduce greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions by drawing carbon into the soil. In this way, soil health management practices can both make soils more resilient and adaptive—a plus for farmers—and mitigate the effects of climate change. The following information is adapted from American Farmland Trust’s Soil Health Stewards training on COMET-Planner.
Identify Carbon Management Emissions Tool Components
COMET is a tool for measuring and managing carbon sequestered in the soil. COMET, which stands for CarbOn Management Emissions Tool, is an online platform comprised of several components: COMET-Planner, COMET-Farm, and COMET-Energy. If you are considering utilizing the COMET tool, you may want to consult the COMET training resources, which include guidance on deciding which COMET component to use. The COMET components continue to be updated regularly.
COMET-Planner
COMET-Planner provides a quick estimate of the GHG mitigation impacts of implementing conservation practices. It is intended to be used for planning purposes. It is based on a larger-scale area, estimating impacts over Major Land Resource Areas. A positive value generated by COMET-Planner represents an increase in carbon sequestered or decrease in GHG emissions. A negative value generated represents either a decrease in sequestered carbon or an increase in GHG emissions. Watch the COMET-Planner Demonstration for an overview of how to use this tool.
The output of the COMET-Planner calculator will be in tons of CO2 sequestered or released. To make sense of this number, the EPA’s Greenhouse Gas Equivalencies Calculator can be used to translate tons of CO2 into more concrete terms, such as the annual CO2 emissions of cars, households, and power plants. This component can be a useful communication tool when developing a conservation plan or evaluating targets.
COMET-Farm
COMET-Farm is an in-depth, site-based, whole farm assessment that accounts for soil properties, weather, farming systems, and management strategies. COMET-Farm can be used for all types of operations, including more complex production systems. The COMET-Farm tool requires more input on the front end, so may take more time to set up, but the reports generated by the tool are more detailed, providing users with projected estimates of baseline “business as usual” emissions, future management scenario emissions, and the change in emissions between these two scenarios.
COMET-Energy
COMET-Energy allows users to calculate the reductions in GHG emissions based on fuel savings. This would often be used as a supplement to COMET-Planner or COMET-Farm because some of the practices in these tools do not incorporate fuel savings. You can enter annual energy savings in gallons, CCF, or kilowatts and COMET-Energy will generate a summary of energy savings, measured either in MMBTU or CO2-reduced.
The COMET suite has provided the groundwork for other tools for identifying GHG-reducing agricultural practices. For example, the USDA’s Climate-Smart Agriculture and Forestry (CSAF) Mitigation Activities List, which includes practices that have a quantifiable mitigative benefit, is informed by the COMET platform. The COMET emissions calculations also inform the Carbon Reduction Potential Evaluation Tool (CaRPE), a tool designed by AFT and ARS scientists to visualize and quantify net GHG emission reductions from the implementation of cropland and grazing land conservation management practices.
Engaging Producers and Landowners
As land protection professionals, considering strategies for tactful communication and relationship-building is key to engaging producers and agricultural landowners. This is especially true when it comes to guiding farmers and ranchers towards the adoption of new practices. The following information is adapted from American Farmland Trust’s Soil Health Stewards trainings on Engaging Landowners and Operators and Working with Diverse Owners and Operators.
Build Farmer Networks
Farmer networks are an important—and trusted—source of information for producers. Helping farmers and landowners identify and tap into existing networks is a good way to communicate information about land management and conservation practice implementation.
As you work to facilitate connections for producers, it is helpful to recognize farmers’ other trusted information sources and think about how these sources can be tapped.. Farmers may rely on neighbors, local farmers’ cooperatives, their local land trust, cooperative extension services, or their local NRCS office for information.
One example of a farmer network is the New York Demonstration Farms Network. This partnership, spearheaded by AFT and NRCS, involves collaboration between researchers, agricultural and conservation organizations, and the farming community. The goal of the network is to allow farmers in the region to learn from one another and to see which practices are most cost effective and have the biggest impact on conservation. Demonstration plot videos and online documentation of the field trials help make demonstrations more widely available. The findings from several of the demonstration farms are captured in the New York Soil Health Case Studies.
Identify Soil Health Messengers
Finding producers willing and well-positioned to participate in field days and other demonstrations can be invaluable. These producers can serve as “messengers,” leading communication within their communities around specific soil health building practices and their personal experiences in adopting them. The following are qualities to keep in mind when identifying these messengers:
- Key leaders in an agricultural community will likely be well-connected and well-respected by other producers.
- Those who have been farming for multiple years may have experiences that are seen as being more credible.
- Producers with good recordkeeping can provide valuable information on their operation over time.
- Farmers who have implemented soil health practices with significant “before and after” contrasts will have more impactful stories to convey.
- A producer with multiple conservation practices in place or one who implements best practices may have an operation more readily able to serve as a model farm.
- Participants must be willing to share their experience publicly—including what didn’t work on their farm.
- Ideal participants are willing to travel and speak about their process in front of their peers.
Finding producers prepared to serve as soil health messengers and building relationships with these partners will take time and patience. To begin identifying these essential communicators, you may want to tap into existing networks. It can help to have a running list of producers in the area who fit the requirements and/or have expressed interest in sharing their experiences and expertise. If you are interested in launching a farmer network, see AFT’s Peer Network Training Toolkit.
Communicating One-on-One with Producers
Strategic communication around soil health practices can make information-sharing with farmers more effective. Approach your outreach to a farmer or rancher as an opportunity to foster a relationship and build a foundation of trust; you can then provide information as appropriate. At any stage in your communications, keep in mind that soil health is likely just one part of the bigger picture for the producer, who may be navigating multiple, concurrent day-to-day challenges on their farm. The following are specific strategies for communicating with producers about soil health:
- Provide evidence of soil health practice benefits. Specific examples, either from a local farmer or publications such as AFT’s Soil Health Case Studies, can make a compelling case for adopting new practices. When visiting a farm or speaking in-person, have a printout of the information to leave with the farmer so they can revisit the resources on their own time. In addition to printouts, podcasts, YouTube, and other widely accessible (and “multi-taskable”) resources may prove helpful for producers with limited time. Pointing to specific resources may also help to address common misconceptions around soil health practices. You may also want to prioritize farmer-led resources when communicating with a producer, such as pointing them to field days or farmer-led organizations in their area.
- Tailor your message to the farm and their specific concerns. One way to approach the conversation is by asking the farmer about their recent successes and challenges. This allows you to acknowledge what is working well for them. If the producer seems receptive, you can also provide suggestions in response to their identified challenges. Having knowledge of the programs and practices most relevant to your audience may result in more meaningful conversation.
Considering the terminology being used by the producer is another means of tailoring the conversation to your audience. For example, farmers may speak of weather-related challenges without talking about climate change. In that case, building on-farm resiliency in the face of extreme weather might be one entry point to discussing soil health. - Build trust over time with your audience. Approach your conversations with producers as a partner, and be sure to indicate support, especially when offering input or suggestions—avoid telling the farmer how to farm. Offering to tour the property with the landowner or producer may make for more impactful visits and if there are issues to be addressed, talking through concerns can be more productive in a face-to-face meeting. If they have an easement on the land and you represent the entity responsible for monitoring, let the producer know ahead of time when you’ll be visiting the farm and invite them to join you. To avoid intimidation, you could have a third party, such as another producer from the area, join for the farm visit as well. If possible, having a staff person who consistently monitors the same easements, rather than different staff visiting the easement, can help facilitate trust. Lastly, having patience is important. Keep in mind that farmer decision making is complex, and you likely won’t convince a producer to overhaul their practices with one visit.
Communicating with Ranchers
Providing evidence, tailoring your message, and building trust are important when speaking with any producer about soil health—including ranchers. It’s important to keep in mind, though, that ranchers may have unique motivations for incorporating soil health practices onto their operations. Namely, a rancher may want to know how building soil health can contribute to healthier forage for their livestock. Ranchers may also face unique challenges in implementing these practices. For example, maintaining enough forage to keep the soils covered can be difficult, especially in semi-arid environments in the West. It can also take years longer to see results from soil health measures in these arid zones.
For these reasons, connecting producers with rancher networks and other resources is especially important. Technical and financial assistance provided through NRCS programs is one place to start (see the tab on “Connecting Producers and Landowners to Soil Health Technical and Financial Resources” for more information on programs relevant to ranchers). The STAR Program provides an implementation framework for conservation practices for producers in the Midwest and western states. Finally, publications like Progressive Forage, a monthly digital magazine, may also provide ranchers with information on implementing and maintaining practices on their land.
 Connect
Connect
STAR Conservation Program
Engage Historically Underserved Producers
Historically underserved farmers and ranchers include beginning, veteran, limited resource, and socially disadvantaged producers (a term defined in the U.S. Code and used in several parts of the federal Farm Bill). To effectively engage historically underserved producers, take time to better understand their particular needs and challenges.
The following considerations and strategies are worth keeping in mind when connecting with any producer, but are especially important when working with historically underserved farmers and agricultural landowners:
- Collaborate with community-based organizations that already serve these groups to inform how you might approach this work. These organizations will have insights into the needs and challenges of your audience.
- Listen to the producer or landowner’s expertise before you make recommendations. Take time to understand their operation and considerations.
- Respect differences in experience. Being mindful of a producer or landowner’s unique perspective can foster trust and create opportunity for both parties to learn from each other.
- Think about whether your audience sees themself in existing resources and consider adapting your resources for their type of operations. Historically underserved producers may operate more diverse farms and ranches on smaller parcels of land and need resources that mirror their operations with more accuracy.
- Program goals may unintentionally exclude certain groups. For example, metrics that prioritize leveraging more program dollars may hinder limited resource producers from participating. Prioritizing faster implementation timelines or favoring greater acreage enrollment may similarly preclude building relationships with historically underserved producers or those on smaller operations.
Host a Field Day
While one-on-one conversations may be the most direct means of relaying information, other forms of communication may be more effective in sharing about soil health practices with a broader audience. Field days and learning circles are ways to relay information to producers and allow producers or landowners to share information with their peers. Below are some tips for organizing a field day or learning circle:
- Consider the ideal time of the year given your location: farmers might have more time to attend a field day in the winter, though there may be less in production on the farm. For farm demonstrations, the end of August may also be a good time, as the visit may be more impactful if participants can see the operation in full swing.
- Look for producer contact lists: some states have lists of producer contacts for purchase for a nominal fee.
- Communicate through different avenues: in addition to digital promotion of your field day, consider sending out postcards or mailings to reach more producers.
- Co-host with partners: invite partner organizations to present and have them help with outreach. This may make for a more engaging field day and attract a wider audience.
- Consider your audience: pick topics that are relevant to farmers in the area and vary the topics and presenters if planning for multiple field days.
- Engage producers as speakers: having a farmer panel where producers can share their experience may be valuable, as they can speak to the concerns and interests of farmers in the area.
- Keep it brief: depending on the size and demonstration, allotting four hours for your field day should be plenty. Providing lunch or coffee and unstructured time for farmers to talk to each other can be valuable.
Agricultural Conservation Easements and Referenced Plans to Encourage Soil Health
Agricultural land protection practitioners are finding ways to promote soil health practices with owners of permanently protected agricultural land. Learn about key considerations as you work to encourage conservation goals through permanent conservation easements. Deepen your understanding of Natural Resources Conservation Service (NRCS) conservation plans and other management plans and learn how these plans can be adapted to engage producers and landowners around soil health. Lastly, learn ways agricultural leases can better support adoption of soil health practices. The following information is adapted from American Farmland Trust’s Soil Health Stewards trainings on Advancing Soil Health Through Agricultural Conservation Easements and Referenced Plans.
Encouraging Conservation and Soil Health in Easements
To encourage conservation outcomes, including those that support soil health, entities initiate conversations early on in easement discussions with their landowners about their conservation goals and objectives. Some have developed educational resources that highlight the benefits of conservation or other management plans as an accompaniment to the easement. Others use questionnaires to better understand landowner priorities.
In addition, easement holders tend to:
Focus on outcomes instead of practices. Many easement holders use deed language on conservation outcomes in the purpose section and in sections about allowable agricultural uses and activities. They may also recommend or require management of the land under easement in accordance with a referenced conservation or management plan. This approach provides a more flexible alternative to mandating specific practices or management systems in the deed itself. It allows for changes to the operation and recognizes that best management practices can evolve over time. If one of the stated conservation outcomes is healthy soils, the conservation or management plan can be tailored to incorporate practices that build soil health.
Require plans to be developed by qualified conservation professionals. Effective conservation planning requires technical expertise. To ensure that referenced plans address specific resource concerns, be sure that plans are written by qualified professionals. NRCS offers a certification for conservation professionals, including staff with conservation districts, who can provide technical service activities according to NRCS standards and specifications for conservation activities. These professionals are certified as Technical Service Providers and listed in a registry maintained by NRCS (see below). Cost-share assistance for the development of conservation plans is available through NRCS.
Use monitoring as an opportunity to encourage conservation. Practitioners consider their capacity to monitor and enforce conservation provisions over time. Some require landowners to follow the practices prescribed in the plan, especially if it is necessary for compliance with federal or state laws or if the plan was developed to address an easement violation. Experienced entities have developed procedures to review and document whether required components of a plan are being followed and have established policies to handle any disagreements. Easement holders may require mediation to resolve disputes; some also allow for the use of qualified third-party experts to help settle differences ahead of engaging in a formal process.
Other organizations view the conservation or management plan primarily as a tool to initiate conversations with producers and landowners and to encourage conservation improvements. If this is the case, practitioners focus on landowner education and note progress toward their conservation goals during monitoring visits.
Learn about Conservation and Other Management Plans
Referencing a conservation or management plan is the most common approach for easement holders to achieve conservation outcomes while providing flexibility for agricultural producers. These plans may apply to portions of or the entire protected area. The plan may satisfy state or federal requirements or may be implemented to advance the entity’s and landowner’s conservation goals. Some easement holders allow the landowner to choose the professional to develop the required plan or plans and require the holder’s approval of the plan; others require the plan drafter to be someone acceptable to both the landowner and easement holder. Many holders require that any plan be updated periodically or when ownership of the eased land changes.
NRCS Conservation Plans
A NRCS conservation plan helps producers and landowners adopt practices and activities that support agricultural production while safeguarding the land and other natural resources. NRCS conservation planners develop plans in collaboration with farmers and ranchers or people who own land used for agriculture. In the case of rented land, either the landowner or the tenant can request a field visit by NRCS.
NRCS uses a multi-step planning process to identify individuals’ conservation objectives, assess site conditions, and identify natural resource concerns. The process also outlines practices and activities to address resource concerns, which are listed in the NRCS Field Office Technical Guide for each state. Plans are developed collaboratively with the landowner or producer and include recommended conservation practices tailored to the land’s unique natural resources and to the individual objectives of the producer or landowner.
In general, NRCS planning assistance is free to farmers or ranchers and agricultural landowners. Most conservation planning efforts, however, are tied to the agency’s priorities as established by state technical committees. These advisory committees may prioritize certain resource concerns, places, or other outcomes within a state. NRCS conservation planning activities also are linked to implementation of the agency’s financial assistance programs. In some counties, individuals who want a conservation plan are placed on a waiting list.
As noted above, NRCS also certifies Technical Service Providers (TSPs), who can provide technical service activities according to NRCS standards and specifications for conservation activities. NRCS lists TSPs in their registry.
Entity Management Plans
Farmland protection entities, like land trusts or state or local governments, often require conservation or management plans as a condition of their easement. Some entities have in-house conservation planners that will draft management plans in collaboration with the producer or landowner; others hire qualified conservation professionals to do so. Farmland protection entities may or may not use NRCS standards and specifications to inform their plans.
Integrate Soil Health
A conservation plan can enable you to initiate conversations about soil health. You can talk to operators and agricultural landowners with existing plans about adding specific soil health goals and practice recommendations in the plan.
Soil Health Management Plans
A Soil Health Management Plan (SHMP) identifies concerns related to the physical, biological and chemical properties of the soil. It provides a framework for working with producers and landowners to adopt activities that will help them maintain or improve the health of the soil on a specific site. NRCS has developed the specifications and standards for a SHMP but does not typically offer this type of planning assistance. Entities, however, can engage a technical service provider (TSP) to develop a SHMP.
Conservation planners pay close attention to land that is prone to erosion (i.e., highly erodible land). To address soil health, NRCS now also considers soil organic matter depletion, aggregate instability, and habitat loss for organisms living in the soil. Planners will propose practices to address identified resource concerns. Then producers and landowners decide what they are able and willing to do, and the plan specifies how the practices can be implemented. Entities can work with producers and landowners to monitor and evaluate practices over time to track progress toward meeting soil health goals.
A key consideration for producers, landowners and easement holders are the costs to implement practices and measure outcomes over time. NRCS has compiled a practice scenario guide for each state that provides estimated costs. TSPs usually know if NRCS has prioritized SHMPs and the practices in the plan in each state. If it is a priority, then cost share assistance would be available.
Use Agricultural Leases to Encourage Conservation
Agricultural leases are legal contracts between a property owner and a tenant that gives the tenant the right to use the land for agricultural purposes for a set period of time. Permanently protected agricultural land may be owned by non-operating landowners or farmers and ranchers who rent their land for agricultural use. The lease agreement outlines the rights and obligations of both parties. The contract aims to protect both parties and help them achieve their goals. This can include improving soil health.
Easement holders can support the development of leases that enhance and emphasize soil health. Easement holders can share information with landowners about ways to encourage adoption of practices that improve soil health.
Key strategies to support conservation on rented land include:
- Establishing regular, open communication. Regular conversations between the landowner and farmer or rancher enable the parties to clarify goals and reach agreement on how to achieve them. To get started, farmers can ask landowners about their future plans for the land. Landowners can ask producers what can be done to reduce erosion or what they would do to protect the soils on their own land. Farmland protection entities can help set up and facilitate these conversations.
- Extending the length of the agreement. Short leases discourage the adoption of conservation practices. Therefore, one of the easiest ways for landowners to encourage conservation is to extend the lease term. Landowners can give producers more time on the land, linking the length of the lease to the time needed to establish and benefit from selected practices. Some experienced easement holders suggest phasing in a longer-term lease when working with a new farmer or rancher.
- Setting specific farming standards. Landowners can be clear about how they expect the land to be managed. The lease can include standards established by state departments of agriculture, soil and water conservation districts and/or practices recommended in a conservation plan. If specific practices are expected, these can be stipulated and defined in the lease to create clear expectations for both parties and help head off confusion. See the links below for sample lease provisions.
- Considering the cost of adoption. Landowners should consider the costs associated with conservation practices, which may include implementation costs, short-term impacts on profits and the cost to maintain practices over time. Consider if the farmer has the necessary equipment to implement the proposed practices. Landowners can encourage adoption by discounting rent, sharing program payments and offering non-monetary incentives like a longer lease. Landowners should learn about the tax treatment of program payments to help inform negotiations.
- Reviewing and revising the agreement. Agree to review and revise the lease on a regular basis. Consider who will have the right to inspect the property and ensure that practices are being implemented. The lease will only work to encourage conservation if it reflects what is happening on the ground.
Connecting Producers and Landowners to Soil Health Technical and Financial Resources
Familiarity with the technical and financial assistance programs offered by the USDA Natural Resources Conservation Service (NRCS) can prove helpful for land protection practitioners who work directly with farmers, ranchers, and landowners. These programs support the implementation of conservation practices, including those that improve soil health, so being able to direct producers and landowners to these resources may improve the likelihood of soil health practice adoption on the land. The following information is adapted from American Farmland Trust’s Soil Health Stewards trainings on Connecting Landowners to NRCS Financial Assistance.
NRCS Conservation Technical Assistance
USDA NRCS provides one-on-one guidance to producers and landowners on conservation techniques and tools via Conservation Technical Assistance, or CTA. The technical assistance offered through CTA often leads to the development of a conservation plan, which is a system of practices that addresses identified resource concerns. Resource concerns are issues related to natural resources on the farm that can be improved through conservation practices.
Conservation planning is the foundation for NRCS financial assistance: producers or landowners applying for these programs work with NRCS state staff to either revise an existing conservation plan or develop a new plan that identifies the natural resource concerns specific to their operation. Those who work with NRCS to implement conservation plans may be directed toward NRCS financial assistance programs if their resource concerns align with available funding.
NRCS Financial Assistance Programs
NRCS offers several financial assistance programs for implementing conservation practices, all of which can be accessed through the NRCS Conservation Program Application. This section focuses on EQIP and CSP, two NRCS programs that most directly address the implementation of conservation practices on working lands.
Environmental Quality Incentives Program (EQIP)
EQIP provides financial and technical assistance for implementing practices that address natural resource concerns and improve working lands. Through EQIP, NRCS works one-on-one with producers and landowners to install NRCS-approved conservation practices, many of which support soil health.
Under EQIP, each NRCS conservation practice has an associated payment rate, which is the rate at which producers will be reimbursed for implementation. In addition to NRCS national resource concern priorities, each state also maintains a list of priority conservation practices for funding; applications that address national and/or state conservation priorities will generally be ranked higher for funding. EQIP also offers higher payment rates for historically underserved participants, including socially disadvantaged, beginning, limited resource, and veteran beginning farmers.
Conservation Stewardship Program (CSP)
Producers who have already implemented conservation practices and want to build upon their efforts can enroll in CSP. Through CSP, NRCS works with producers to develop a conservation plan that enhances existing practices. CSP participants earn payments for maintaining their existing conservation work and for incorporating new conservation practices and/or enhancements into their operation. For example, a producer who plants cover crops may choose to enhance this practice by incorporating multi-species or deep-rooting cover crops.
Through both EQIP and CSP, NRCS technical assistance is offered at no cost. NRCS staff and Technical Service Providers help enrolled producers with developing conservation plans for their operations, and with planning, designing, and implementing conservation practices. More information on these programs can be found on the NRCS EQIP and CSP pages online.
Applying to NRCS Conservation Programs
A landowner or producer interested in EQIP or CSP should reach out to their local NRCS field office. NRCS staff or a Technical Service Provider can work with them to evaluate the current management system, natural resource concerns, and the options available to them. When applying for a conservation program, the producer, the land, and the practice must all meet NRCS eligibility criteria. Field office staff can assist prospective applicants with determining eligibility.
Before receiving financial assistance through NRCS, the producer or landowner will also need to establish farm and producer records with the Farm Service Agency (FSA). NRCS can work with an applicant to establish their farm records.
Once a landowner or producer decides to apply, they can submit a Conservation Program Application (NRCS-CPA-1200) to their local field office and NRCS will work with them to either revise an existing conservation plan or develop a new conservation plan. Keep in mind that states announce sign-up deadlines for consideration for funding. There are typically multiple continuous cut-off dates for each program.
Applications may be prioritized through a screening process to identify those that have maximum conservation benefits. Applications are then ranked based on alignment with national and state resource concerns. The highest-ranking applications are selected for funding, until available funding is exhausted. An accepted application results in a contract. The participant then arranges to install, implement, or construct the practices. After implementation, NRCS field staff will certify the implementation/installation prior to authorizing reimbursement. The producer is expected to maintain the practice for the duration of the practice lifespan specified by NRCS.
Funding Opportunities for Entities
NRCS also offers partnership programs geared towards entities. The Regional Conservation Partnership Program (RCPP), which addresses natural resource concerns on agricultural land, is one such program. When an organization applies for RCPP funding, they identify the specific resource concerns they want to address and the value of cash or in-kind contributions they can provide as match. Landowners can then apply to the funded RCPP projects in their region if their resource conservation concerns align with the project. Conservation Innovation Grants (CIG) is another program for entities. CIG is a targeted grant program; proposed projects must meet the description of innovative conservation projects or activities published in the annual funding notice.
State Departments of Agriculture or Departments of Natural Resources may also offer funding to entities or landowners to do conservation work. By maximizing existing sources of conservation funding, an entity can better support landowners who seek to implement soil health building practices. Offering producer grants designed to supplement existing sources of funding is another way entities can make the most of available conservation dollars.
Conservation programs for grazing lands
Pastureland and rangeland can be enrolled in NRCS conservation programs using the application process outlined above. The conservation or Grazing Management Plan that the landowner develops will be unique to their land. When working with NRCS, field staff may refer a rancher to the Conservation Reserve Program, depending on their goals for their land. The Conservation Reserve Program, or CRP, is administered by the Farm Service Agency (FSA) and supported by NRCS and the U.S. Forest Service. The program allows producers and/or landowners to take privately owned land out of annual production for 10-15 years. In exchange, FSA pays annual rental payments, as well as cost-share and incentives for establishing and maintaining perennial cover. There are different enrollment options under CRP; grasslands CRP focuses on protecting grasslands and promoting sustainable grazing practices. Land under easement can be enrolled in CRP if the easement terms do not contain a resource-conserving provision and do not restrict agricultural uses. The easement will need to be reviewed before the CRP can be approved. It is also possible for land enrolled in CRP to be placed under easement if the entity holding the conservation easement certifies that they are aware of the land enrolled in CRP and that the participant will be able to comply with CRP provisions.
Leveraging Ecosystem Markets to Finance Soil Health Practices
Private sources of funding, including ecosystem markets, provide another tool for scaling up soil health systems on agricultural land. Ecosystem markets—and specifically carbon markets—have expanded in recent years, so if you are a land protection practitioner who works with farmers and landowners, you may be getting questions from your partners about how these markets work, and whether they are eligible to participate. The following information is adapted from American Farmland Trust’s Soil Health Stewards trainings on Leveraging Private Funding to Finance Soil Health Practices.
Ecosystem Markets
Ecosystem markets involve payments to landowners to protect, restore, or mitigate impacts to ecosystems. This exchange is usually between an entity that has a negative ecosystem impact and an entity that has a corresponding positive impact. The following section will focus primarily on carbon markets.
Carbon markets trade in carbon credits—the measurable reduction of GHG emissions from an activity or project that is used to compensate for emissions occurring elsewhere. Typically, credits are measured in metric tons of carbon dioxide equivalents, or CO2e.
Carbon markets involve a buyer and a seller. Corporations are typically the “buyers” and farmers implementing climate-beneficial practices are a “seller” in carbon markets. Agriculture and forestry are the only economic sectors that naturally sequester carbon in plants, trees, and soils.
Carbon market developers “broker” the transaction of carbon credits between buyers and sellers. Different entities will have different focuses within ecosystem markets, as well as different incentives, varied payment structures, and different levels of technical support.
The role of farms in carbon markets
Current research suggests that some cropland management practices, including those that support soil health, can sequester carbon, making farmland an important carbon sink. Cover cropping and no-till are two examples of practices that store carbon and benefit soil health.
Farmers who are interested in taking part in carbon markets may wonder how much carbon their farm can store. This depends on a variety of factors, including farm- and field-level characteristics such as soil type, climate, and topography. The management systems in place, including crop rotations, the depth of tillage, and residue and nutrient management, may also make a difference.
Considerations Prior to Entering an Ecosystem Market
For farmers who are considering participating in an ecosystem market, there are a variety of factors that will determine which market is the right fit for them. These markets are designed to pay farmers for carbon capture beyond an operation’s baseline activity, a concept referred to as “additionality”. Essentially, this requires that the on-farm practices generating the carbon credit be newly implemented. Keep in mind that, depending on the operation, the farmer may receive higher payment rates for implementing certain practices, like no-till and cover cropping, through an incentive program like EQIP as opposed to a carbon market. Ecosystem markets could make sense for a farmer who was already planning to implement a new practice on their operation, but market payments alone may not be sufficient to justify on-farm management changes. In some cases, it is possible to “stack” benefits, that is, to get a carbon market payment on top of a public program payment, such as through EQIP. This may increase the return on investment for implementing a new practice. Owners of permanently protected agricultural land should review their conservation easement to decide whether provisions prevent participation in a carbon market. Some deed requirements might limit opportunities for additionality.
If you’re working with a landowner who is thinking about entering a carbon market, also be sure that they are informed when it comes to:
- Their goals for participating in carbon markets, and the payments they would receive.
- The management changes that would be required of their operation to sequester a certain amount of carbon.
- The level of technical support they would need and what types of support are available through the market.
- The recordkeeping necessary for participation in these markets.
Preparing Producers to Participate in a Carbon Market
For those who are ready to enter an ecosystem market, it may be too early to enroll the whole farm—these markets are evolving, so you might suggest that the farmer enroll a few fields at a time. When entering into a market, a producer will ideally be prepared with some conservation agronomy resources, as they will need technical assistance with implementing conservation practices. You can also encourage producers to get their farm records ready, as having detailed data is key to receiving the highest payment rates.
Lastly, when it comes time to review a contract, the producer should read the fine print, and ideally will have a lawyer review a contract with them prior to entering a carbon market. Contract items to consider include:
- Does enrollment in a carbon market limit eligibility for other financial incentives? Generally, private and public sources of funding can be stacked, but this may not always be the case.
- Contract length, and whether there is a penalty for breaking the contract early.
- Whether rented lands are eligible to enroll in the market, and if so, how the program is structured with regards to the landowner and the renter.
- Price stability or price caps: payment schedules may be subject to market volatility, or a producer may be locked into the contract incentive rate.
- Privacy and data management transparency.
- Verification fees or other hidden fees. In particular, find out who is paying the costs for third party verification.
Above all, ensure that you aren’t jeopardizing your trust or relationship with the producer when discussing programs like carbon markets, as there are still some significant caveats related to these markets. Specifically, much of the research to date has been conducted on surface soils, which leaves questions as to what carbon storage looks like deeper in the soil profile. Practice permanence is an issue, as sequestration is only of benefit if the carbon is stored indefinitely. Ecosystem markets are also a rapidly changing landscape, with new partnerships still forming. Many entities currently involved have rolled out pilot phases in different areas and are still in the process of determining what the full roll-out of their market looks like. Given these uncertainties, practitioners and producers will be best served to approach these markets cautiously.